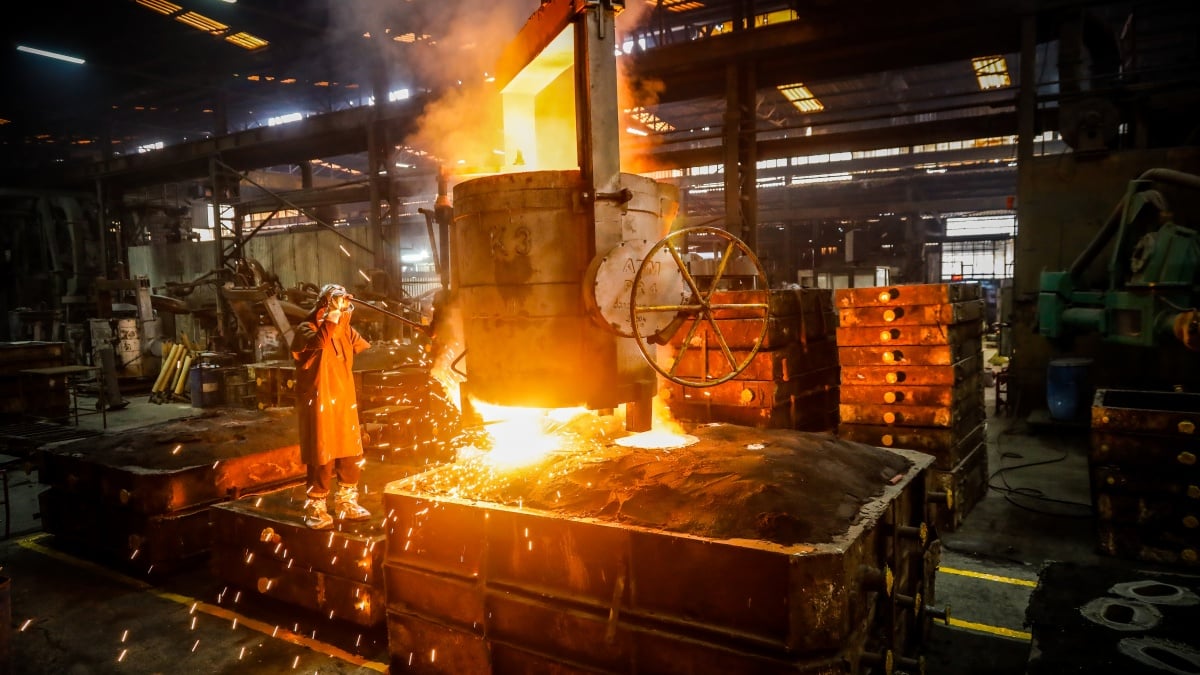
As successful casting processes are based on a proper casting process design, this blogpost discusses the relevance of the planning of the casting process, the design of the gating system and the function of a cooling system.
As the mold production for sand casting is a highly complex four step process, we'll discuss each step in a separate blogpost continuing with the second step of the production which is the casting process design.
After having found the right mix for the molding material, the design of the casting process can start. This design is based on various factors, including the quality requirements of the castings, the production batch, and the production conditions. To optimize the casting process design, the following points are crucial:
- Understanding customer needs
- Familiarity with the existing production conditions and equipment options
- Economic analysis of products
- Energy-saving and environmental protection
Planning the casting process carefully
It is important to understand that each casting process is individual in its own way. The design of the parameters of the casting process is therefore a complex and highly professional step in which numerous factors must be taken into account. Especially for castings with a complex structure, it is useful for the casting engineer to work closely together with the designer.
Furthermore, the sand casting process should be carefully planned. In particular, it is important to determine the pouring location in advance. This is because the pouring position has, among other things, an influence on the solidification process, the flow field, and the temperature field. Other points to consider are the determination of the parting surface, the number of castings, and the minimum size of the castings.
How can cavities be formed in the casting?
In order to form intentional cavities in the casting, the help of so-called sand cores is sometimes needed. These are designed in advance and are built into the mold. In addition to the sand core, a sand core rejection system must also be designed to get the sand out of the casting afterward. After casting, the sand core is broken to create a cavity. However, the construction of such sand cores is very time consuming, which is why they are avoided whenever possible.
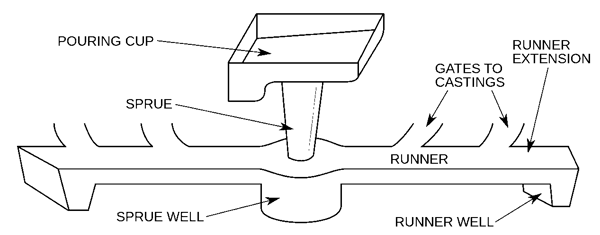
What needs to be considered when designing the gating system?
While the design of the sand core is usually optional, the design of the gating system is always required. Designing it correctly is a difficult but very important task. Around 30% of the casting waste is caused by a faulty design of the gating system. During the design process, it is therefore important to ensure, among other things, that the molten metal can fill the cavities in time. In addition, the molten metal must flow evenly - but not too quickly. Furthermore, the filling pressure must be sufficiently high and the in-runners must be correctly positioned. Many other parameters play a role, which is why the successful completion of this step is based on many years of experience.
Functions of the riser and the cooling system
The riser plays an important role in the casting process. It is an additional part that stores extra liquid metal. This is necessary because during the solidification phase the volume of the alloy changes and without a riser, it is possible for shrinkage holes to form. Depending on the alloy, the design of the riser changes. For alloys with a low volume change, a rather small riser is used, which mainly discharges gas. For alloys with a high volume change, a cylindrical riser is used to compensate for the volume shrinkage. This is positioned so that it is above the thickest part of the casting, as this is the last part to cool down.
The so-called chills also play an important role in the cooling process. They serve to increase the local cooling rate. A distinction is made between two different types of chills. Outer chills are placed outside the model. They, therefore, do not fuse with the casting and can be reused several times. In contrast, inner chills are placed in the mold and fuse with the casting. They are only used if the chilling effect from the outside is not sufficient, which is the case, for example, with particularly thick castings. Accordingly, inner chills are rarely used.

With over one hundred years of experience in the production of sand castings, AMPCO METAL has perfected the casting process design and has been delighting its customers for decades with castings of reliable and high quality.
If you want to dive deeper into the world of copper and copper alloys, download a free extract of our book "Metallurgy of Copper and Copper Alloys". It is a compilation of metallurgical work made on copper and copper alloys that has been produced in collaboration with metallurgy expert Piet Wenschot.




